Causes of constant accumulation of mucus in the throat and methods of treatment
With mucus in the throat is an unpleasant condition during which a thick exudate accumulates in the oropharynx. This is a fairly common phenomenon that, perhaps, every adult has encountered with banal colds, SARS, etc.
The condition gives the patient a lot of discomfort: a person cannot swallow, speak normally, suffers from a sore throat in most cases. There may be a sensation of a lump in the throat.
Dealing with thick mucus in the throat is not easy. It is necessary to find the root cause of the phenomenon and eliminate it. What do you need to know about the factors in the development of mucus in the throat and how to get rid of it?
Mucoid secretion (otherwise mucus) is produced by goblet cells located in the thickness of the epithelium of the mucous membrane.
The universal mechanism of its formation in the throat is as follows:
- The mucous membrane of the oropharynx is affected by a pathological exogenous (external) or endogenous (internal) factor. This may be an inflammatory process, the impact on the anatomical structures of chemical reagents, high temperatures.
- A natural defensive reaction occurs - the body actively produces mucus in order to get rid of an imaginary or real pathological agent and its waste products, in other words, strive to wash it off.
- The more intense the impact, the stronger the exudation.
Non-infectious causes
The causes of excessive secretion of mucus in the throat are many and most of them are infectious. However, there are other factors associated with pathologies of the stomach, allergic reactions. Let's consider them in more detail.
Drip syndrome
Most often we are talking about the common cold of non-infectious genesis in the chronic stage, allergic and vasomotor.
These forms of it are manifested by the flow of nasal mucus into the vestibular region of the throat and larynx (postnasal drip syndrome, English postnasal drip), the symptoms are aggravated at night and in the morning. After waking up, a short-term intense cough is possible, caused by irritation of the reflexogenic zones from excess exudate.
On visual examination, no signs of inflammation of the oropharynx are observed, however, characteristic mucous cords are visible on the back of the throat.
During the day, the symptoms disappear, because in the upright position, the mucous secretion does not accumulate, but flows freely into the trachea and is swallowed without affecting the receptors responsible for the cough reflex.
Intensive smoking
Experienced smokers are well aware of the sensation of a lump in the throat when thick, poorly discharged mucus accumulates.
The reason for its occurrence is the effect on the oropharynx of tobacco hot smoke and tar. Permanent burns are formed. The body tries to get rid of the negative influence by producing exudate.
At the same time, viscous mucus constantly accumulates not only in the throat, but also in the bronchi, as well as the lungs of smokers. You can cope with this condition only by giving up cigarettes and tobacco products.
This is not so easy to do, but after a while everything falls into place.
allergic reactions
Allergies affecting the oropharynx are quite common (about 15% of all allergic reactions occur here).
The formation of a false immune response goes through several stages:
- penetration of the antigen
- adhesion of the antigen to the antibody and the formation of a single complex,
- release of histamine and damage to cells and tissues.
Allergy is accompanied by a mass of symptoms, in addition to the accumulation of viscous mucous exudate. This is a feeling of tickling, burning, shortness of breath (increase in the number of respiratory movements per minute), suffocation (impaired respiratory function of varying severity), pain behind the sternum, swelling of the larynx (fraught with the development of obstruction and asphyxia).
The immune response can be dangerous to the life and health of the patient. Exudation, as in the previous case, is due to the effect on the epithelium.
Gastritis

The disease is an inflammation of the walls of the stomach. The mucosa degrades, ulcerative defects gradually form.
During the pathological process, a number of characteristic symptoms appear. Accumulation of a large amount of mucus in the larynx in the morning, pain behind the hailstone and in the epigastric region, which is aggravated by eating.
Dyspeptic phenomena (burning behind the sternum, the so-called heartburn, nausea, vomiting, intolerance to odors, problems with stools).
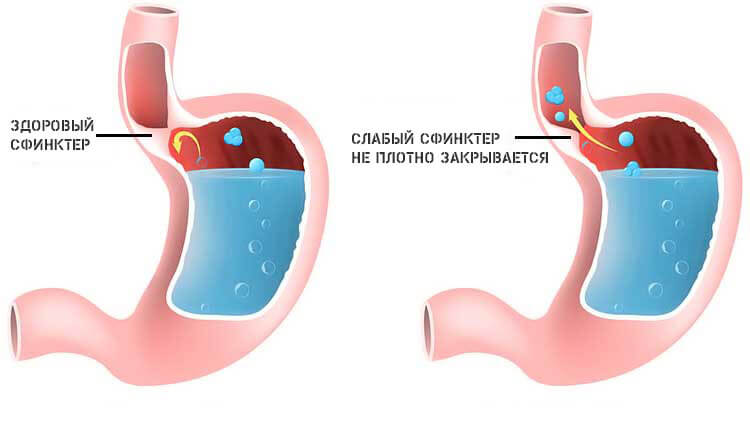
Reflux esophagitis
Throwing of gastric contents from a hollow organ back into the esophagus. This pathology is characterized by weakness of the lower esophageal sphincter and has a mixed origin, but is of considerable danger.
People with reflux are known to be more likely to develop esophageal cancer. In addition, breathing problems (asphyxia, suffocation) and death are possible if liquid stomach contents leak into the lungs. Especially because reflux occurs mostly at night.
Mucus is produced in response to the impact on the epithelium of the acidic juice of the stomach, it is collected in the esophagus in excess, especially when a person is lying down.
stomach ulcer
If mucus accumulates in the throat, the cause may be a stomach ulcer. With it, as with gastritis, heartburn develops, belching of acidic contents and other symptoms.
The essence of the pathological process is the formation of an ulcer defect on the epithelium of a hollow organ.
The accumulation of mucus in the vestibule of the throat in this case is the lesser of evils. If the disease is not cured in time, perforation (perforation of the stomach wall) is possible.
Alcohol abuse
"Chronic" long-term use of alcohol leads to the formation of persistent burns of the mucous membrane of the oropharynx. The result is the production of a large amount of exudate.
To cope with this condition, it is enough to stop drinking ethyl alcohol. The maximum allowable amount of ethanol per day is 30-50 ml, no more. Only quality wine, no vodka or beer. Otherwise, the mucous mass in the throat will accumulate constantly.
Indirectly affects the formation of mucus in the throat and trachea consumption of large amounts of spicy food. As a rule, hot spices and dishes are rich in capsaicin or sulfur compounds.
They irritate the mucous membranes of the oropharynx, causing intense exudation. This, in general, is quite physiological, but an unpleasant phenomenon.
infectious factors
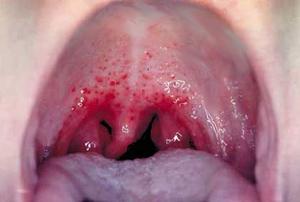
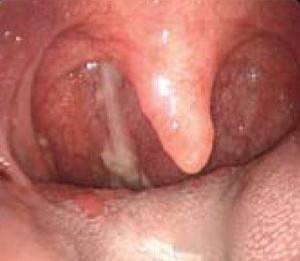
The most common pathology is tonsillitis or inflammation of the palatine tonsils. The second name of the disease is angina.
The soft palate may also be involved in the pathological process. It is characterized by intense pain in the oropharynx, itching, burning, inability to eat normally.
Hyperemia of the pharynx develops, the structure of the pharynx becomes loose. There is an intense production of mucus.
In this case, pus, a substance with an unpleasant odor, is always released. Requires complex treatment. In the absence of therapy, problems with the heart and lungs are possible (with a downward spread of the infectious agent).
- Laryngitis. Inflammation of the mucous membranes of the larynx. It is characterized by pain behind the sternum, a strong barking cough, which is not stopped by standard means, and excessive secretion of mucus.
- Tracheitis. Inflammatory lesion of the trachea. Symptoms are similar to laryngitis.
- Pharyngitis. Inflammation of the mucous membranes of the throat. Always characterized by intense exudation.
- Bronchitis, pleurisy and pneumonia. In this case, mucus is formed not in the throat, but in the lower respiratory tract (this is sputum) and, when coughed up, enters the oropharynx.
- Nasopharyngeal lesions. Primarily . Mucus runs down the back of the nose and accumulates in the throat. This is the most difficult state in terms of prospects.
- sinusitis in general. Inflammation of the paranasal sinuses (frontal sinusitis, sphenoiditis and ethmoiditis). They are characterized by the flow of sticky mucous exudate into the throat without coughing (it is observed only in the morning), similar to post-nasal syndrome. The pathological process itself does not affect the larynx, therefore, redness of the back wall and pain are not observed.
In all the cases described, the body in this way tries to get rid of pathogenic microorganisms and their metabolic products.
Associated symptoms
The release of mucous exudate is always accompanied by some manifestations. They are multiple.
Only the most common are presented:
- pain behind the sternum, in the throat. Increases when swallowing, eating.
- respiratory disorders. Problems with inhalation or exhalation due to swelling of the anatomical passages.
- constant swallowing.
- bad breath. Due to the active reproduction of the bacterial flora.
- violations of nasal breathing, pain in the projection of the sinuses.
- persistent cough or occasional coughing.
By itself, the exudate may be clear or purulent, yellow, viscous or liquid. It all depends on the underlying disease.
Which doctor should I contact?
Doctors of various specialties are involved in diagnosing the causes of the development of exudation in the throat. First of all, it is recommended to go to an appointment with a therapist.
He will tell you in which direction to move, what and how to examine and which specialist to go to next. The therapist performs routine diagnostic measures.
In the future, you will need to contact a specialized doctor:
- otolaryngologist. For problems with the nasal passages and oropharynx, they usually turn to him.
- gastroenterologist. He deals with problems with the gastrointestinal tract. Treats gastritis, ulcers and reflux esophagitis.
- pulmonologist. In the event that the lungs or the lower respiratory tract in general are affected, one cannot do without consulting this doctor.
You may also need to consult a neurologist (for problems with the central or peripheral nervous system), an endocrinologist (in some situations, the production of mucus in the throat may be due to problems with the thyroid gland). In any case, it is not recommended to hesitate to visit a specialist.
At the initial appointment, specialists identify the characteristic complaints of the patient by conducting an oral survey.

In modern clinics, standard questionnaires and questionnaires are used for these purposes. An anamnesis is also taken. The doctor, as part of this process, reveals what the patient has suffered or is suffering from.
It is especially important to clarify the facts of the presence in the recent past of infectious diseases, possibly occurring in the chronic stage.
Finally, it is the turn of instrumental and laboratory studies:
- General blood analysis. Shows the inflammatory process, but it is impossible to determine in which part of the body. There is an increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, an increase in the concentration of leukocytes (white blood cells). With allergies, an increase in the number of eosinophils occurs. This is a direct indication of the immune response.
- Biochemical analysis of venous blood. It also shows the inflammatory process.
- Throat swab. It is carried out in all cases.
- Sowing of biological material (smear) on nutrient media. In other words, bacteriological research. Allows you to accurately determine the pathogen, if any, to determine its sensitivity to antibiotics. This makes it possible to accurately determine the therapeutic tactics.
- Histological examination of the cells of the mucous membrane of the throat. Smokers may develop cellular atypia, which is dangerous because it is fraught with cancer.
- FGDS. An unpleasant but necessary examination of the stomach and esophagus. It is carried out to assess the state of anatomical structures visually.
- endocrine tests. Analyzes for T3, T4, TSH.
- Allergic tests. They are not cheap, but they allow you to determine the sensitivity of the body to allergens of a particular nature.
- stress tests. The patient is confronted with the allergen directly. This study is carried out only under the supervision of a competent specialist within the hospital.
In the system of these studies, it is quite enough, but neurological tests may be needed if nerve pinching is suspected in osteochondrosis, which causes false
Symptomatic therapy
From home methods, drinking plenty of warm liquids will help alleviate the condition. This is an effective way to thin the mucus and wash away excess mucus.
However, this is only a temporary measure.: Exudate production will continue as the underlying cause has not been corrected.
Treatment of the underlying cause begins after the diagnosis and administration of appropriate medications. There can be no single list of drugs, since treatment regimens differ from disease to disease.
Therapy for bacterial infections
Infectious inflammation of the oropharynx caused by bacterial flora is stopped by drugs from several pharmaceutical groups.
The following list of medications is indicated:
- Anti-inflammatory nonsteroidal origin. As the name of the group of these drugs implies, they are designed to relieve general and local inflammation. Taken in the form of tablets. With fragility of blood vessels and a tendency to bleeding, care must be taken. Suitable medicines such as Ketoprofen, Diclofenac, Ibuprofen and its analogues.
- Antibacterial agents. They form the basis of the treatment of all bacterial lesions (in this case, the oropharynx). Specific names are assigned only by a doctor and are applied in the system. First you need to determine the type of bacteria and its sensitivity to drugs. Taking these medicines uncontrollably, the patient risks his own health and even life.
- Analgesics. Used to relieve pain. New generation drugs based on metamizole sodium are prescribed: Baralgin, Pentalgin.
- (secretolytics) and . The former enhance the cough reflex, which contributes to the rapid discharge of exudate. Mucolytics thin the viscous mucus - it becomes larger, but more liquid consistency, which facilitates expectoration.
Treatment of noncommunicable diseases
Endocrine pathologies (primarily thyroid diseases) are treated with iodine preparations. In the absence of iodine deficiency, a diet poor in this element is prescribed.
If the reason lies in bad habits, you need to stop smoking, alcohol. It is recommended to regularly humidify the air in the room and carry out wet cleaning.
Gastroenterological pathologies are treated with proton pump inhibitors, wound healing drugs and antacid agents (only for gastritis with high acidity).
Reflux is treated in the same way. In addition, special gymnastics is prescribed.
The appearance of a mucous secretion in the throat is an unpleasant symptom. By itself, it does not require treatment - you need to eliminate the root cause and this is the only way to get rid of constant discomfort.
